4N25S: A Versatile and Affordable Optocoupler for Galvanic Isolation
Galvanic isolation is crucial in various applications to ensure separation between two signals. The 4N25S optocoupler offers an inexpensive solution to this challenge, with a fast rise time of 2 microseconds. In this article, we explore the features and benefits of the 4N25S, shedding light on its internal structure, isolation voltage, transmission speed, certifications, and availability.
Understanding Optocouplers
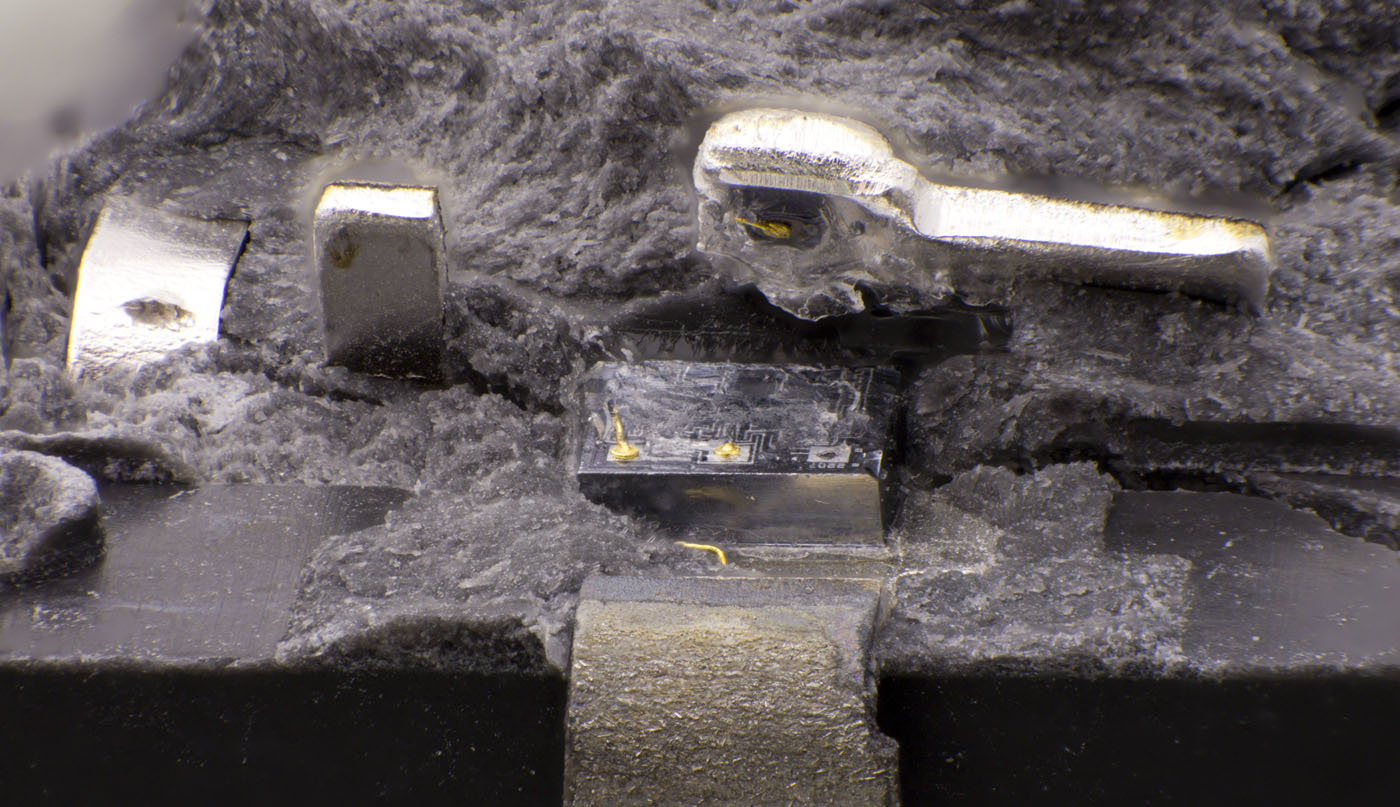
To grasp the role of an optocoupler, let's examine the semiconductor decapitation image from https://www.richis-lab.de/Opto01.htm. This image reveals that optocouplers combine a diode and a photosensitive conductor in a light-proof housing. This unique construction allows the control signal to influence the "sensing side" without the need for a direct electrical connection.
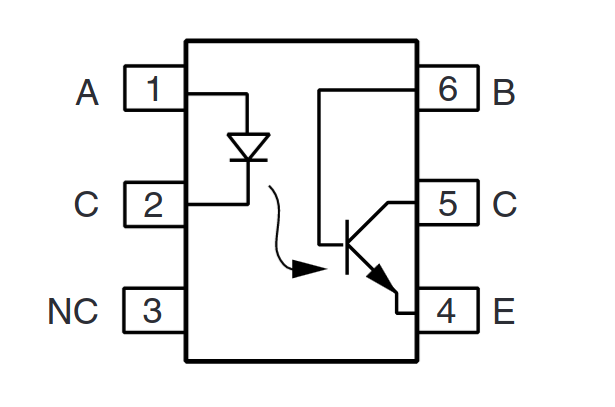
Internal Structure and Active Element
A closer look at the 4N25S datasheet reveals its internal structure, as shown in the figure. The 4N25S utilizes a phototransistor as its active element. This component plays a crucial role in achieving galvanic separation.
Isolation Voltage and Transmission Speed
Optocouplers are designed to provide galvanic separation, although physical limitations set boundaries on the maximum level of isolation between the input and output sides. The 4N25S boasts an isolation voltage of 5000V. Additionally, the semiconductor processes involved in the phototransistor enable a reaction speed specified with a rise/fall time of 2 microseconds, indicating the optocoupler's maximum bandwidth.
Certification Level
The 4N25S optocoupler tends to have widespread certifications. For instance, Lite-On, a manufacturer of the component, has obtained approvals such as:
- UL approved (No. E113898)
- TUV approved (No.R9653630)
- CSA approved (No. CA91533-1)
- FIMKO approved (No. 193422)
- NEMKO approved (No. P96103013)
- DEMKO approved (No. 303985)
- SEMKO approved (No. 9646047/01-30)
- VDE approved (No. 094722 )
These certifications validate the optocoupler's compliance with industry standards and ensure its reliability.
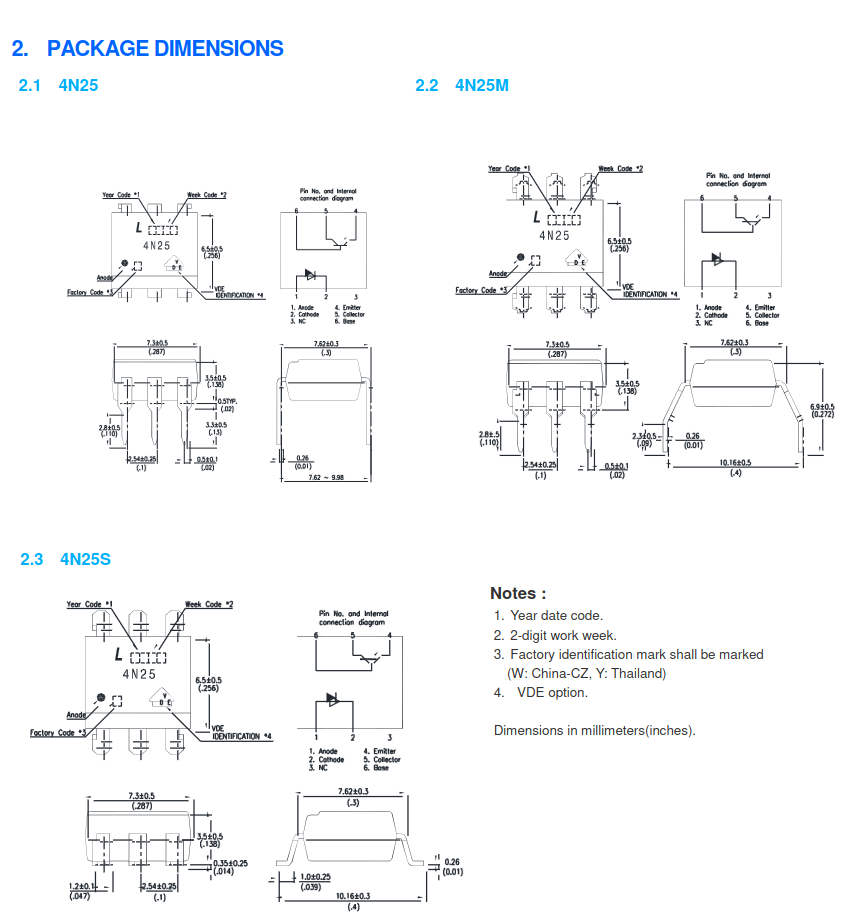
4N25 vs. 4N25S
The 4N2x family of components, including the 4N25, has a long-standing presence in the market. The 4N25S, found in a surface-mount package, shares the same die as the traditional DIP housed 4N25. The primary difference lies in the lead arrangement, which is optimized for reflow soldering in the S version of the component. Lite-Ons version of the datasheet, found at https://optoelectronics.liteon.com/upload/download/DS-70-99-0010/4N2X%20series%20Datasheet%201115.pdf, provides the overview shown in the figure below.
Inventory Availability
As of now, an OEMSecrets distributor search reveals ample stock of the 4N25S from major distributors. In quantities of 100, the individual part costs around 25 euro cents (correct as per the date of publication). Additionally, multiple second-source vendors offer the 4N25S, ensuring a steady supply regardless of a specific semiconductor foundry.
Conclusion
When a generic optocoupler is needed for an application, the 4N25S emerges as a highly accessible and reliable choice. Its wide availability and performance make it an attractive option. Moreover, the presence of multiple semiconductor vendors manufacturing the part reduces the likelihood of shortages. With the 4N25S, achieving galvanic isolation becomes more convenient and cost-effective in a range of applications.